Image
Edit on GitHub| S | Return | Name | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image | (void) | ||
| Image | (const Image& image) | ||
| Image | ( Image&& image) | ||
| Image | (const Size& size) | ||
| Image | (uint16 w, uint16 h) | ||
| bool | IsValid | (void) const | |
| bool | Create | (const Size& size) | |
| bool | Create | (uint16 w, uint16 h) | |
| void | Destroy | (void) | |
| uint16 | GetWidth | (void) const | |
| uint16 | GetHeight | (void) const | |
| uint32 | GetLength | (void) const | |
| uint32* | GetData | (void) const | |
| uint32 | GetLimit | (void) const | |
| Color | GetPixel | (const Point& point) const | |
| Color | GetPixel | (uint16 x, uint16 y) const | |
| void | SetPixel | (const Point& point, Color c) | |
| void | SetPixel | (uint16 x, uint16 y, Color c) | |
| bool | Fill | (const Color& color) | |
| bool | Fill | (uint8 r, uint8 g, uint8 b, uint8 a = 255) | |
| bool | Swap | (const char* sw) | |
| bool | Flip | (bool h, bool v) | |
| Image& | operator = | (const Image& image) | |
| Image& | operator = | ( Image&& image) | |
| bool | operator == | (const Image& image) const | |
| bool | operator != | (const Image& image) const |
Description
Represents a cross-platform and hardware-independent two-dimensional image. An image can be created through the Constructor or Create functions but in both cases, data is allocated using width and height. To check whether an image has been created, use the IsValid function. Use the Destroy function when the image is no longer needed to free up any used resources, although it is also called by the destructor automatically.
When creating an image that's already been created, if the current length of the pixel data is greater than the new length, then only the dimensions get set, and the pixel data remains unmodified. If, however, the current length is less than the new length, the image gets destroyed, and new data gets allocated.
Image metrics are available through accessor functions like GetWidth, GetHeight, and GetLength. To get access to the pixel data directly, use the GetData function which returns a one-dimensional array of packed ARGB integers. Alternately, GetPixel and SetPixel can also be used to manipulate the pixel data.
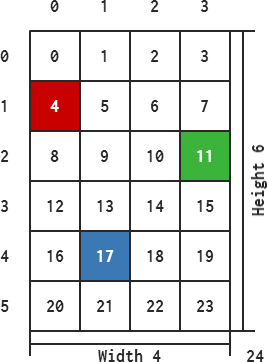
Image image (4, 6);
image.Fill (0 );
uint32* data = image.GetData();
image.GetWidth (); // 4
image.GetHeight(); // 6
image.GetLength(); // 24
data[ 4] = 0xFFC80000;
data[11] = 0xFF3CB43C;
data[17] = 0xFF3C78B4;
image.GetPixel (0, 1); // (200, 0, 0)
image.GetPixel (3, 2); // ( 60, 180, 60)
image.GetPixel (1, 4); // ( 60, 120, 180)
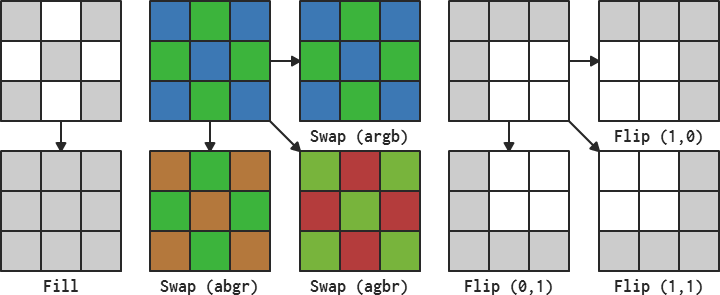
The Image class provides additional functionality for manipulating the image. The Fill function, for instance, can be used to fill the entire image with a color while the Flip function can mirror the image vertically or horizontally. Individual channels of pixels can be swapped using the Swap function; this is especially useful for when the channels need to arranged in a specific order.
The Image class supports deep copying, move semantics, and deep comparison. Where appropriate, the image gets copied in its entirety; the now independent copy has the same width and height as the original. In instances where a copy is inefficient, a move is used instead, allowing the class to behave like a regular POD type.
Constructors
| Image | (void) |
Constructs an image with all components set to zero.
| Image | (const Image& image) |
| Image | ( Image&& image) |
Constructs an image by copying or moving the contents of image.
| Image | (const Size& size) |
| Image | (uint16 w, uint16 h) |
Constructs an image with width and height set to size or w and h.
Warning: Data is uninitialized, use the Fill function to initialize the data prior to use.
Functions
| bool | IsValid | (void) const |
Returns true if this image has been created.
| bool | Create | (const Size& size) |
| bool | Create | (uint16 w, uint16 h) |
Creates a new image with width and height set to size. If this image has already been created and the current length of the pixel data is enough to accommodate the new length, then only the dimensions get set, and the pixel data remains unmodified. If, however, the current length is less than the new length, then this image gets destroyed, and new data gets allocated. If any component of size is zero, this function returns false
Warning: Data is uninitialized, use the Fill function to initialize the data prior to use.
| void | Destroy | (void) |
Destroys the internal pixel data and deletes any memory which might have been allocated. All values including width and height are set to zero. This function does nothing if the image has not yet been created or has already been destroyed.
| uint16 | GetWidth | (void) const |
| uint16 | GetHeight | (void) const |
Returns the width and height of this image.
| uint32 | GetLength | (void) const |
Returns the number of pixels in this image (i.e. width × height).
| uint32* | GetData | (void) const |
Returns a pointer to the pixel data, stored as an array of packed ARGB integers.
| uint32 | GetLimit | (void) const |
Returns the length of the pixel data array, which could be greater than length.
| Color | GetPixel | (const Point& point) const |
| Color | GetPixel | (uint16 x, uint16 y) const |
Returns the Color of the pixel at point. A default Color is returned if point is out of bounds.
| void | SetPixel | (const Point& point, Color c) |
| void | SetPixel | (uint16 x, uint16 y, Color c) |
Sets the Color of the pixel at point to c. Does nothing if point is out of bounds.
| bool | Fill | (const Color& color) |
| bool | Fill | (uint8 r, uint8 g, uint8 b, uint8 a = 255) |
Fills the entire image with color and returns true. Returns false if this image is not valid.
| bool | Swap | (const char* sw) |
Swaps the channels of each pixel in the entire image based on the value of sw and returns true. sw is made up of four case-insensitive letters: r, g, b, and a, arranged in the order the channels should be rearranged in. Passing "argb", for instance, results in no changes because that is the initial order of the channels, but passing "abgr" keeps the alpha and green channels where they are and only swaps the red and blue channels. Returns false if this image is not valid or the format of sw is incorrect.
| bool | Flip | (bool h, bool v) |
Flips the entire image horizontally or vertically depending on the values of h and v and returns true. Returns false if this image is not valid.
Operators
| Image& | operator = | (const Image& image) |
| Image& | operator = | ( Image&& image) |
Copies or moves the contents of image to this image. Prior instances are destroyed.
| bool | operator == | (const Image& image) const |
| bool | operator != | (const Image& image) const |
Performs an equality comparison to determine whether the two images are identical.
Warning: This function can be slow for larger images unless they have different sizes.
Examples
// C++
#include <Robot.h>
ROBOT_NS_USE_ALL;
int main (void)
{
Image image (2, 4);
image.GetWidth (); // 2
image.GetHeight(); // 4
image.GetLength(); // 8
image.GetLimit (); // 8
// GetData allocated
image.Create (4, 6);
image.GetLength(); // 24
image.GetLimit (); // 24
// GetData unchanged
image.Create (4, 2);
image.GetLength(); // 8
image.GetLimit (); // 24
// Fill image with white
image.Fill (0xFFFFFFFF);
// 00AA00, BB00CC, white, white
// 00DD00, EE00FF, white, white
uint32* data = image.GetData();
data[0] = 0xFF00AA00; // (0, 0)
data[1] = 0xFFBB00CC; // (1, 0)
data[4] = 0xFF00DD00; // (0, 1)
data[5] = 0xFFEE00FF; // (1, 1)
// Switch red and blue channels
// 00AA00, CC00BB, white, white
// 00DD00, FF00EE, white, white
image.Swap ("abgr");
// Mirror the image horizontally
// white, white, CC00BB, 00AA00
// white, white, FF00EE, 00DD00
image.Flip (true, false);
// Create new copy
Image copy = image;
copy.GetPixel (2, 0); // 0xFFCC00BB
copy.GetPixel (3, 0); // 0xFF00AA00
copy.GetPixel (2, 1); // 0xFFFF00EE
copy.GetPixel (3, 1); // 0xFF00DD00
image == copy; // True
image != copy; // False
copy.Destroy();
image == copy; // False
image != copy; // True
return 0;
}
// Node
var robot = require ("robot-js");
var image = robot.Image (2, 4);
image.getWidth (); // 2
image.getHeight(); // 4
image.getLength(); // 8
image.getLimit (); // 8
// getData allocated
image.create (4, 6);
image.getLength(); // 24
image.getLimit (); // 24
// getData unchanged
image.create (4, 2);
image.getLength(); // 8
image.getLimit (); // 24
// Fill image with white
image.fill (0xFFFFFFFF);
// 00AA00, BB00CC, white, white
// 00DD00, EE00FF, white, white
var data = image.getData();
data[0] = 0xFF00AA00; // (0, 0)
data[1] = 0xFFBB00CC; // (1, 0)
data[4] = 0xFF00DD00; // (0, 1)
data[5] = 0xFFEE00FF; // (1, 1)
// Switch red and blue channels
// 00AA00, CC00BB, white, white
// 00DD00, FF00EE, white, white
image.swap ("abgr");
// Mirror the image horizontally
// white, white, CC00BB, 00AA00
// white, white, FF00EE, 00DD00
image.flip (true, false);
// Create new image clone
var copy = image.clone();
copy.getPixel (2, 0); // 0xFFCC00BB
copy.getPixel (3, 0); // 0xFF00AA00
copy.getPixel (2, 1); // 0xFFFF00EE
copy.getPixel (3, 1); // 0xFF00DD00
image.eq (copy); // True
image.ne (copy); // False
copy.destroy();
image.eq (copy); // False
image.ne (copy); // True